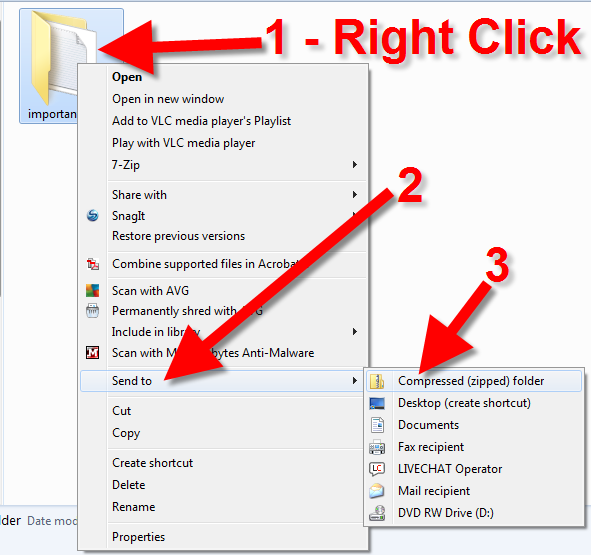
This compression system is a very handy invention, especially for Web users, because it lets you reduce the overall number of bits and bytes in a file so it can be transmitted faster over slower Internet connections, or take up less space on a disk. A compressed file is any file with the compressed attribute turned on. Using the compressed attribute is one way to compress a file down to a smaller size to save on hard drive space, and can be applied in a few different ways (which we talk about below). Compressing a file is computationally intense, so the more you try to compress a file, the longer it takes to compress. Users have to choose between how much they want a file to compress and how long it will take to do the compression. Command Prompt does let you copy and paste from it so you can paste the output into a text file, or just use followed by the name of a text file to save the output to. Compressing files and folders. You can compress files and folders from the Windows GUI but the compact command can also compress them if you run it with the /c modifier.
- What Does A Compressed Zip Folder Do
- How To Open A Zip File
- How Does Zip File Work
- What Does A Compressed Folder Do
Summary :
What is the Enable file and folder compression option in Disk Management? Should you select this option? In this post, MiniTool will discuss the Enable file and folder compression option. Read it now and decide whether to enable File and Folder Compression.
Quick Navigation :
Enable File and Folder Compression
To save disk space, most people may choose to delete unnecessary files or to compress the disk to reclaim free space. In terms of compression, we have discussed 'should you compress your OS drive'. If you want to compress your system partition, it is worth reading this post.
Here we will focus on another compression option. That is 'Enable file and folder compression'. What is it? Should you use it? When should you use it? How to use it? Keep reading and the following content will answer all the questions.
What Is 'Enable File and Folder Compression'?
'Enable file and folder compression'is an option in Disk Management and it shows up when users create a partition or format a partition via Disk Management.
What Does the Option Do and Work?
What does the Enable file and folder compression do? How does file compression work? These two questions are frequently asked by lots of Windows users.
For the first question, the answer is that this option will compress everything on the partition, as well as any new files added later.
But how does this option work? You may have noticed that the option is available if the partition adopts NTFS file system; it is greyed out if not.
What's the relationship between the Enable file and folder compression option and NTFS file system? The option compresses the entire partition with Windows File Compression that is a part of the NTFS file system (used by the Windows operating system has a built-in compression feature known as NTFS compression).
So, we could make a conclusion. That is you actually use the technology of NTFS compression when ticking the Enable file and folder compression option.
The compression process is that NTFS compresses files and folders by first driving the data streams into CUs (control unit). After the stream contents are created or changed, the CU in the data stream will automatically be compressed individually.
Further reading:
The compression algorithms in NTFS are designed to support the cluster size of up to 4KB. In other words, when the cluster size is greater than this number on an NTFS partition, NTFS compression is unavailable.
Comparing the NTFS compression rate with that of other compression tools on the market, like 7-Zzip, the former performs not well but it has indeed safe.
What Does A Compressed Zip Folder Do
The following table from the website shows the comparison between these two compression tools. Note that it is not recommended that users compress the files and folders related to the system although the make an experiment on these folders.
| Compression Tools | Folder | Original Size | Compressed Size | Savings in percent |
| 7-Zip | Program Files (x86) | 17.4GB | 10.2GB | 40.3% |
| Program Files | 8.5GB | 3.1GB | 60.5% | |
| Windows | 15.1GB | 3.2GB | 78.8% | |
| NTFS compression | Entire Drive | 70.9GB | 58.4GB | 17.6% |
What're the Benefits and Drawbacks of the Option?
There is no perfect thing and the option is not excluded. Although enabling file and folder compression could be helpful when you receive low disk space warning, you may have the following troubles.
- When you move a file that has been compressed by NTFS compression to another location, the file will be decompressed, then moved and finally compressed again. The file will also be expanded before they are transferred over the internet so this may even make things slower.
- The option fails to work when you want to compress the files that already are compressed. In truth, in the most detrimental circumstance, enabling file and folder compression to compress the files that have been compressed can make these files bigger.
- Frequent compression can also affect your drive performance.
When to Tick Enable File and Folder Compression?
Compressing files and folders can help you reclaim a lot of disk space in the best of circumstances. In other words, this option may make things worse if you are using it in suitable situations.
The compression is ideal for the following situations.
1. The files you want to compress are rarely used. The reason is that slow-down of access may be not noticeable if you never access the files. However, the following kinds of files SHOULD NOT be compressed.
- Windows system files and other program files. Compressing these files can affect your computer's performance and bring about other errors.
- The files are in uncompressed format. What does that mean? For example, Office documents, text files and PDF files can undergo a compressed format, while the MP3 files or videos are already saved in a compressed format.
- The files you want to compress have already been in the compressed format. For example, if you want to compress the Office documents, text files and PDF files, or audio or video files by ticking the Enable file and folder compression option, you will not see much improvements.
- The directory which you want to compress has games along with its installation files. This will make the fetch timings of the gaming module become longer and your game will lag drastically.
2. You want to reclaim space on a small SSD.
In other words, it is worth to enable file and folder compression on SSD (featuring a small storage capacity) as this will cause more writes to this drive. But keep in mind that frequently using compression on SSD may shorten the drive's life.
3. Your computer is equipped with fast processors.
As we know, the compressed files need to be uncompressed when you want to use them. Furthermore, the files need to be compressed again after you use them. This is time-consuming if your processor is not as fast as possible.
If your computer features a high CPU usage, you should not use NTFS compression. When you using file and folder compression on the computer with a high CPU load, the CPU load of the computer will increase and it takes long to access to the files.

The following table from the website shows the comparison between these two compression tools. Note that it is not recommended that users compress the files and folders related to the system although the make an experiment on these folders.
| Compression Tools | Folder | Original Size | Compressed Size | Savings in percent |
| 7-Zip | Program Files (x86) | 17.4GB | 10.2GB | 40.3% |
| Program Files | 8.5GB | 3.1GB | 60.5% | |
| Windows | 15.1GB | 3.2GB | 78.8% | |
| NTFS compression | Entire Drive | 70.9GB | 58.4GB | 17.6% |
What're the Benefits and Drawbacks of the Option?
There is no perfect thing and the option is not excluded. Although enabling file and folder compression could be helpful when you receive low disk space warning, you may have the following troubles.
- When you move a file that has been compressed by NTFS compression to another location, the file will be decompressed, then moved and finally compressed again. The file will also be expanded before they are transferred over the internet so this may even make things slower.
- The option fails to work when you want to compress the files that already are compressed. In truth, in the most detrimental circumstance, enabling file and folder compression to compress the files that have been compressed can make these files bigger.
- Frequent compression can also affect your drive performance.
When to Tick Enable File and Folder Compression?
Compressing files and folders can help you reclaim a lot of disk space in the best of circumstances. In other words, this option may make things worse if you are using it in suitable situations.
The compression is ideal for the following situations.
1. The files you want to compress are rarely used. The reason is that slow-down of access may be not noticeable if you never access the files. However, the following kinds of files SHOULD NOT be compressed.
- Windows system files and other program files. Compressing these files can affect your computer's performance and bring about other errors.
- The files are in uncompressed format. What does that mean? For example, Office documents, text files and PDF files can undergo a compressed format, while the MP3 files or videos are already saved in a compressed format.
- The files you want to compress have already been in the compressed format. For example, if you want to compress the Office documents, text files and PDF files, or audio or video files by ticking the Enable file and folder compression option, you will not see much improvements.
- The directory which you want to compress has games along with its installation files. This will make the fetch timings of the gaming module become longer and your game will lag drastically.
2. You want to reclaim space on a small SSD.
In other words, it is worth to enable file and folder compression on SSD (featuring a small storage capacity) as this will cause more writes to this drive. But keep in mind that frequently using compression on SSD may shorten the drive's life.
3. Your computer is equipped with fast processors.
As we know, the compressed files need to be uncompressed when you want to use them. Furthermore, the files need to be compressed again after you use them. This is time-consuming if your processor is not as fast as possible.
If your computer features a high CPU usage, you should not use NTFS compression. When you using file and folder compression on the computer with a high CPU load, the CPU load of the computer will increase and it takes long to access to the files.
For the question 'Should I enable file and folder compression', do you have any own answer after reading the above content? Think twice before you use Enable file and folder compression.
How to Use 'Enable File and Folder Compression' on Windows PC
You can use NTFS compression to make files smaller and then some disk space will be back if your situation meets the following three requirements simultaneously.
Note that you can use the Enable file and folder compression option only when your partition has been set to NTFS file system or will be set to this file system.
In the following content, we will discuss two cases you may face when you want to use this option.
Case 1: Compress NTFS File System Partition and Files
When creating an NTFS partition or formatting a partition to NTFS, you just need to check the box next to the Enable file and folder compression option. The option will automatically compress everything on the new partition.
To compress the files and folders in NTFS partition or this partition, you can refer to How to Use NTFS Compression Windows 10.
Case 2: Compress Non-NTFS File System Partition and Files
As we know, the five kinds of Windows file systems are FAT12, FAT16, FAT32, NTFS and exFAT and the latter three is wildly used. Here we would like to focus on the latter three kinds of file systems.
How about compressing FAT32 and exFAT file system partitions by using the Enable file and folder compression option in Disk Management?
It is sure that you can convert these FAT32 and exFAT partition by formatting them to NTFS with Disk Management and tick the Enable file and folder compression option. This is convenient, whereas this also causes data loss.
But cheer up as there is another way you can adopt to finish this conversion without data loss.
Here is the full guide of NTFS vs FAT32 vs exFAT. Check out this post to know the differences.
Convert FAT32 to NTFS without data loss
When it comes to converting FAT32 to NTFS, it is highly recommended that you try MiniTool Partition Wizard that can help you make this conversion without data loss. Furthermore, this program can also help you resize partitions with ease when your free disk space becomes smaller.
Here is the tutorial on how to convert FAT to NTFS without data loss via MiniTool Partition Wizard.
Step 1: Download MiniTool Partition Wizard by clicking the following button, install it and then launch it to get its main interface.
Step 2: Look at the Disk Map and highlight the FAT32 partition you want to compress and then select the Convert FAT to NTFS feature from the left panel.
Step 3: Confirm the information on the new pop-up window and then click the Start button to begin the conversion process.
After the three steps and click the Close button, you will see that FAT32 has been successfully converted to NTFS. Then follow the guide mentioned in How to Use NTFS Compression Windows 10.
Convert exFAT to NTFS without data loss
As for converting exFAT to NTFS, the conversion process is completely different from the above conversion process.
If you want to compress the whole exFAT partition without important data loss, you can move the important files or folders to another location and then format this partition to NTFS with Disk Management. Please do not forget to tick the Enable file and folder compression option.
You can move these files easily with the following steps.
Step 1: Open your File Explorer and expand your exFAT partition.
Step 2: Select the file you want to remove to another location and then click the Home tab > Move to.
Step 3: Scroll down the drop-down menu until you see the Choose Location option and then choose the location you want from the new window.
Step 4: Repeat the operations until you transfer all the important data.
If you just want to compress some large files or folders in this partition, you can move them to the NTFS partition and then activate NTFS compression to compressed these files.
In truth, using an external hard drive will often make sense than using compression. The reason is that more capacity means more room to store files and never have to feel the compression and decompression process that can affect system performance.
Logic pro x sidecar. This article introduces some great 8TB external hard drives and some easy and effective ways to manage them.
Bottom Line
It is safe to use NTFS compression to reclaim disk space back. But keep the ideal situations for using NTFS compression in mind when you want to tick the Enable file and folder compression option in Disk Management.
Has this post answered all the questions of the Enable file and folder compression? If not, please leave your questions in the following comment zone and we will answer the questions as soon as possible.
If you run into some issues when you convert FAT32 to NTFS and back up the exFAT partition with MiniTool Partition Wizard, please contact us via [email protected].
Enable File and Folder Compression FAQ
When you are in the following situations, you can enable file and folder compression.
- The files you want to compress are rarely used.
- The files are in uncompressed format.
- You want to reclaim space on a small SSD.
- Your computer is equipped with fast processors.
In Windows 2000, as in Windows NT 4.0, there are rules that determine the compression state when you move and copy files and folders within and between volumes. There are also rules that determine the compression state when you move and copy files and folders between FAT and NTFS partitions. Compression is a feature of NTFS volumes only and cannot be performed on a FAT volume.
Copying compressed files and folders can cause performance degradation, because Windows 2000 uncompresses the file, copies it to the new location, and then compresses the file again.
Copying a File within an NTFS Volume
When a file is copied from one folder to another folder within an NTFS volume, the compression setting for the file changes to that of the target folder. Copying a file is like creating a new file in the target folder, so it will take on the attributes of the target folder. For example, if you copy an uncompressed file into a compressed folder, the file will be automatically compressed (see Figure 8.7).
Figure 8.7 When data is copied within an NTFS volume, the data inherits the compression attributes of the target folder.
Figure 8.7 When data is copied within an NTFS volume, the data inherits the compression attributes of the target folder.
Moving a File or Folder within an NTFS Volume
When a file or folder is moved from one folder to another within an NTFS volume, the compression setting is retained. For example, if you move an uncompressed file into a compressed folder on the same volume, the file will remain uncompressed (see Figure 8.8).
Figure 8.8 When data is moved within an NTFS volume, the data retains its compression attributes regardless of the compression status of the target folder.
' ' F | i M | k | fc |
Copying or Moving a File or Folder between NTFS Volumes
When a file or folder is copied or moved from one folder to another on different NTFS volumes, the compression setting for the file changes to that of the target folder. Once again, this happens because when you copy or move a file from one volume to another, it has to create the file at the target and then delete it from the source, so it takes on the attributes of the folder in which it is created (see Figure 8.9 and Figure 8.10).
Figure 8.9 When data is copied between NTFS volumes, the data inherits the compression attributes of the target folder.
4 | SOI | 4 t | > | 4 |
Figure 8.10 When data is moved between NTFS volumes, the data inherits the compression attributes of the target folder.
< * | 53 | > | a |
Moving or Copying a File or Folder from an NTFS Volume to a FAT Volume or to a Floppy Disk
When a file or folder is moved or copied to a FAT volume, it is automatically uncompressed, because FAT does not support Windows 2000 file compression (see Figure 8.11). Floppy disks also do not support compression, as the information needed to support the NTFS file system cannot fit on a floppy, so floppies end up being FAT (see Figure 8.12).
Figure 8.11 When data is moved or copied from an NTFS volume to a FAT volume, the data is automatically uncompressed.
Figure 8.11 When data is moved or copied from an NTFS volume to a FAT volume, the data is automatically uncompressed.
How To Open A Zip File
Figure 8.12 When data is moved or copied from an NTFS
volume to a floppy disk, the data is automatically uncompressed.
Figure 8.12 When data is moved or copied from an NTFS
volume to a floppy disk, the data is automatically uncompressed.
You cannot choose the color for compressed files to be viewed by default, but you can do so with a Microsoft utility called TweakUI (see Figure 8.13). TweakUI is a Windows NT Powertoy that provides access to many hidden registry keys in Windows 95/98/NT/2000. One feature of this utility allows you to set the compressed data color to a different color. Powertoys were developed by Windows developers in their spare time. They are not officially supported by Microsoft, although they work very well. You can find TweakUI by browsing http://www.microsoft.com/windows and looking for Windows NT or 2000 power toys.
How Does Zip File Work
Casino cruise fort lauderdale. Figure 8.13 The Explorer tab of the TweakUl utility includes the option to change the color of compressed files at the bottom of the dialog box. Camera lock 1 5 download free.
Figure 8.13 The Explorer tab of the TweakUl utility includes the option to change the color of compressed files at the bottom of the dialog box.
How to download wow on mac. Continue reading here: Managing Disk Quotas
What Does A Compressed Folder Do
Was this article helpful?

